
- #Ubuntu raid monitor how to
- #Ubuntu raid monitor install
- #Ubuntu raid monitor update
- #Ubuntu raid monitor full
- #Ubuntu raid monitor software
One component of each stripe is a calculated parity block. The RAID 5 array type is implemented by striping data across the available devices. Your RAID 1 array should now automatically be assembled and mounted each boot.
#Ubuntu raid monitor full
Each disk in a RAID 1 array gets a full copy of the data, providing redundancy in the event of a device failure. The RAID 1 array type is implemented by mirroring data across all available disks. Your RAID 0 array should now automatically be assembled and mounted each boot.
#Ubuntu raid monitor update
#Ubuntu raid monitor how to
This section can be referenced to learn how to quickly reset your component storage devices prior to testing a new RAID level. If you wish to follow along, you will likely want to reuse your storage devices after each section. Throughout this guide, we will be introducing the steps to create a number of different RAID levels. These drives do not need to be formatted prior to following this guide. Depending on the array type, you will need at minimum between two to four storage devices. If you are using DigitalOcean, you can use Block Storage volumes to fill this role. As such, you will need some drives to configure. Multiple raw storage devices available on your server: We will be demonstrating how to configure various types of arrays on the server.To learn more about RAID and to get a better understanding of what RAID level is right for you, read our introduction to RAID article.

A basic understanding of RAID terminology and concepts: While this guide will touch on some RAID terminology in passing, a more complete understanding is very useful.To learn how to set up an account with these privileges, follow our Ubuntu 18.04 initial server setup guide. A non-root user with sudo privileges on an Ubuntu 18.04 server: The steps in this guide will be completed with a sudo user.In order to complete the steps in this guide, you should have: In this guide, we will go over a number of different RAID configurations that can be set up using an Ubuntu 18.04 server. Administrators have great flexibility in coordinating their individual storage devices and creating logical storage devices that have greater performance or redundancy characteristics.
#Ubuntu raid monitor software
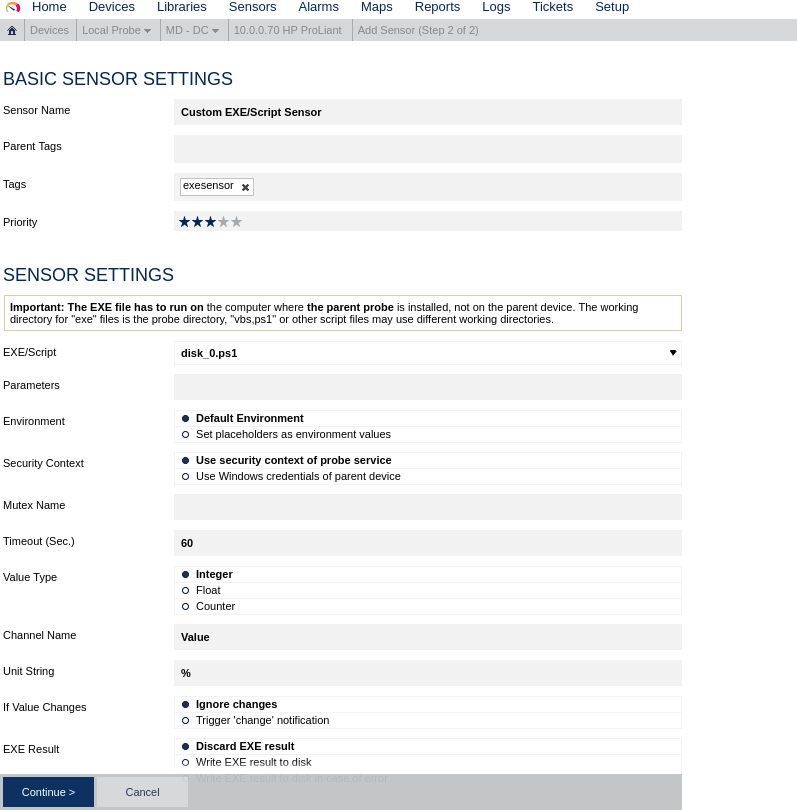
Thanks for reading.Įnter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.The mdadm utility can be used to create and manage storage arrays using Linux’s software RAID capabilities. Let me know if you know a better way of doing this. usr/bin/mailx -s “$email_subject” “$email_recipient” < $log_filename Hpacucli ctrl all show config > $log_filenameĮmail_subject=”Harddrive Failed On $hostname”

If hpacucli ctrl all show config | grep -q “Failed” thenĮcho -e “Harddrive Check Run: `date`” > $log_filenameĮcho -e “\nUsing Command: hpacucli ctrl all show config” > $log_filename Log_filename=”/root/harddrive_check/log/$date.log” # Email Current datetime in YYYY-MM-DD_HH-MM-SS The indentation seems to have got lost but you should be able to recreate it. When configuring Postfix, I selected “Internet Site” and entered the hostname of the server.
#Ubuntu raid monitor install
It will also install Postfix (if this isn’t already setup). This is a virtual package on Ubuntu and I tend to install bsd-mailx. To send an email from command line you will also need mailx. I assume that you have already installed the HP Proliant Support Pack perhaps using these instructions. I am sure that there is a good way of setting this up with Nagios or SMNP – however, I thought I would write a little bash script which emails me if any of the hard drives in the raid array fail. I wanted to monitor our HP server raid array on Ubuntu 12.04.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
